BY DR. SAMSON AUDU
A man’s prostrate gland usually starts to enlarge after he reaches 40 years of age. This condition is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). This is considered a natural process of aging, and attempts to stop or reverse it so far have been unsuccessful.
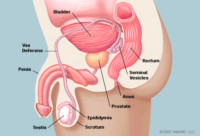
The prostate gland serves a fertility function as it secretes the seminal fluid that helps to nourish and transport the sperm that comes from the testicles. The fluid is then stored in the seminal vesicles. The gland itself surrounds the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine from the bladder out through the tip of the penis. As the prostate grows larger, it may press on the urethra. This narrowing of the urethra can cause some men with prostate enlargement to have trouble with urination. Prostate enlargement may be the most common health problem in men older than 60 years of age.
What Causes an Enlarged Prostate?
The prostate gland, which is normally about the size and shape of a walnut, wraps around the urethra between the pubic bone and the rectum, below the bladder. In the early stage of prostate enlargement, the bladder muscle becomes thicker and forces urine through the narrowed urethra by contracting more powerfully. As a result, the bladder muscle may become more sensitive, causing a need to urinate more often and more suddenly.
The prostate grows larger due to an increase in the number of cells (hyperplasia). However, the precise reason for this increase is unknown. A variety of factors may be involved, including androgens (male hormones), estrogens, and growth factors and other cell signaling pathways (cell-to-cell communication).
As the prostate grows larger and the urethra is squeezed more tightly, the bladder might not be able to fully compensate for the problem and completely empty. In some cases, blockage from prostate enlargement may result in stagnation and backing up of urine, which in turn may cause repeated urinary tract infections, bladder stones, bladder diverticulae (outpouchings or pockets inside the bladder), and gradually result in bladder or kidney damage. It may also cause a sudden inability to urinate (acute urinary retention) — a painful medical emergency that requires urgent drainage
Symptoms of prostate enlargement
• Feeling difficult to urinate
• Urine that stop and start
• Frequent urination mostly at night
• Dribbling to urinate
• Return to urinate minute after minute etc this problem can affect you sexual life and make you grow old quick.
• Straining to urinate
• A urinary strain that start and stop
• Getting up frequently at night
The two essential causes of urinary retention are (1) blockage of the urethra and (2) disruption of the delicate and complex system of nerves that connects the urinary tract with the brain and the nervous system (as described earlier).
Common causes
• Blockage (obstruction): The most common cause of blockage of the urethra in men is enlargement of the prostate. In males, the prostate gland partially surrounds the urethra. If the prostate becomes enlarged, which is common in older men, it presses on the urethra and can block it. The most common cause of prostate enlargement is benign prostatic hypertrophy (often called BPH). Other causes of prostate enlargement include prostate cancer and prostate infection (prostatitis). Causes of blockage of the urethra that can occur in both sexes include scar tissue, injury (as in a car wreck or bad fall), blood clots, infection, tumors in the pelvic region, and stones (rare).
• Call Dr. Samson Audu on 09094957175 or 08062660945
• Office Address: 183, Ipaja Road Baruwa Bus Stop, Ipaja Lagos
• Website: www.thelightherbals.com
• Distance is not a barrier